What is the Hearing Number?
The hearing number
The Hearing Number is a simple metric that gives you a snapshot of your hearing at the time you learn it. Your Hearing Number tells you the softest speech sound you can hear. The number typically ranges from about 0 to 100 decibels (dB). The higher your Hearing Number is, the louder sounds will need to be for you to hear them.
Most children have a Hearing Number that is less than 10, which means they can hear very soft sounds. As we get older, we all lose some hearing, and our Hearing Number increases. You have two Hearing Numbers: one for your right ear and one for your left ear.
The Hearing Number is also known as the pure tone average, or PTA4. The PTA4 is one of many ways that hearing care professionals measure hearing. You may have heard hearing loss described as mild, moderate, or severe. The PTA4 is used to define those broad categories too.
- Mild, which is a Hearing Number of 20 to <35
- Moderate, which is a Hearing Number of 35 to <50
- Moderately severe, which is a Hearing Number of 50 to<65
- Severe, which is a Hearing Number of 65 to <80
Source: World report on hearing. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.

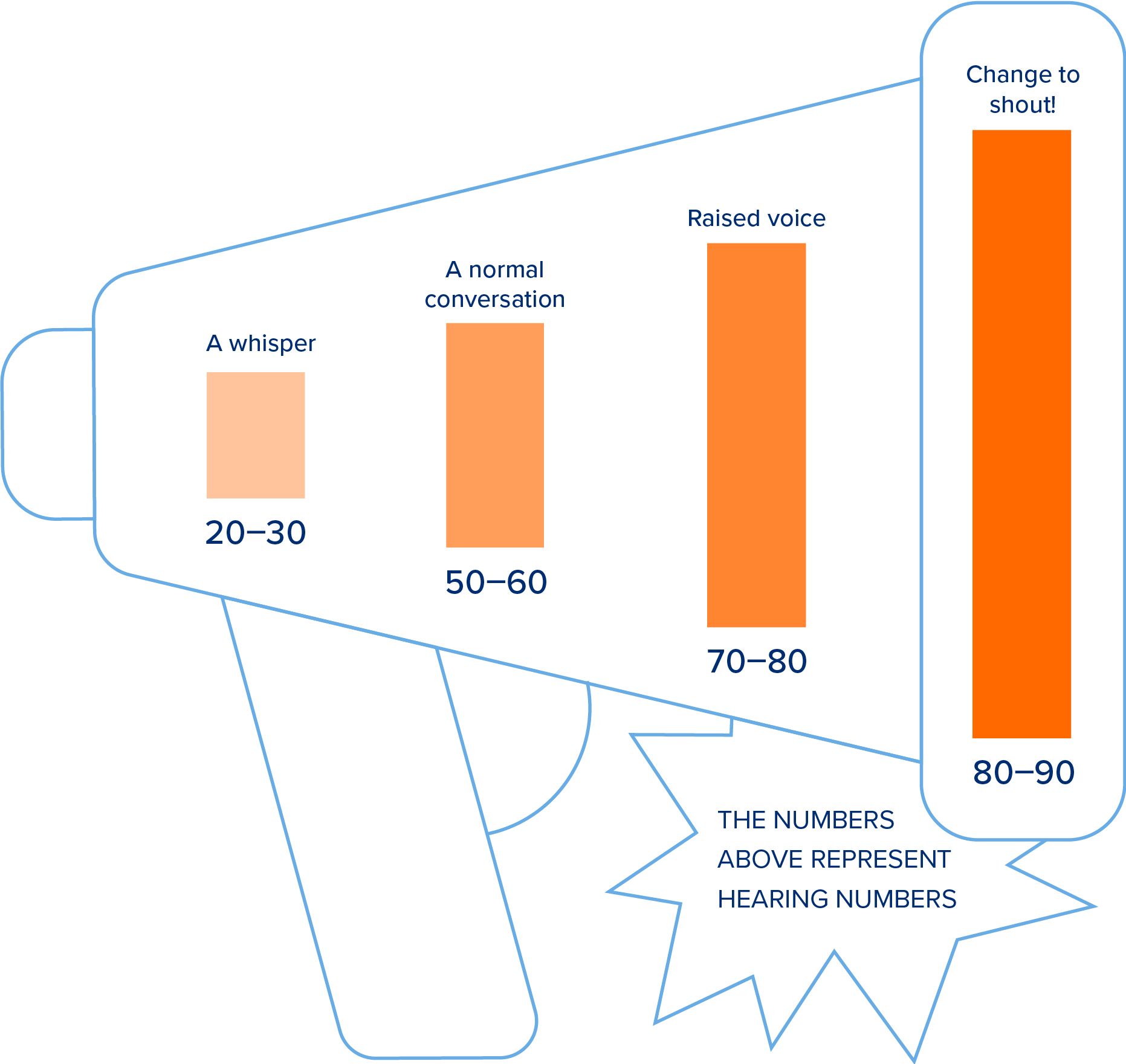
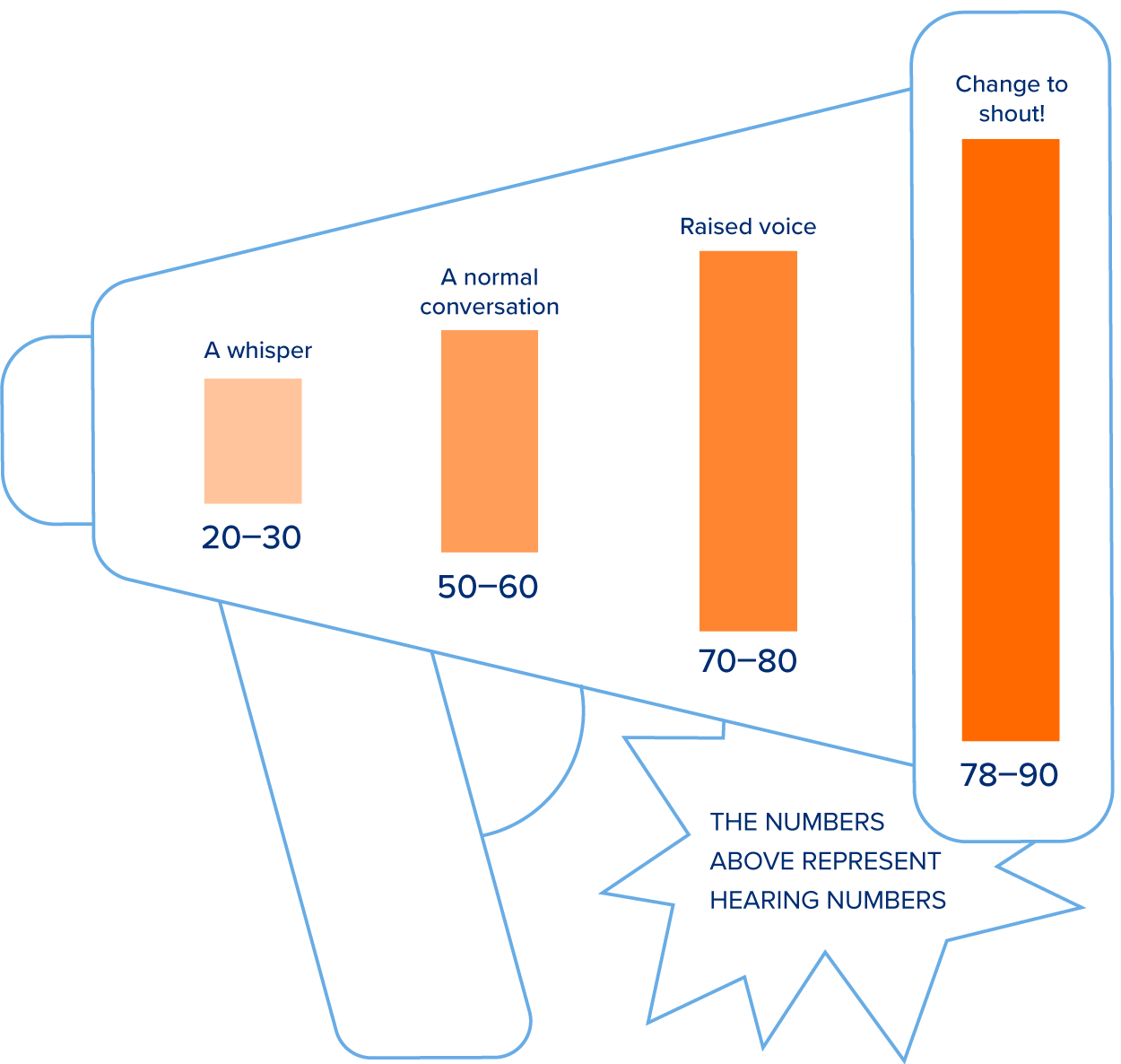
The higher the Hearing Number, the louder your conversations need to be
Why should I know my Hearing Number?
Knowing your Hearing Number is a step toward taking control of your hearing health now and throughout your life. Knowing your Hearing Number will help you:
- Better understand your own hearing with a number that you can monitor over time.
- Know when to start using communication strategies or hearing technologies that will improve your hearing and overall quality of life.
- Feel empowered and more comfortable talking about your hearing with loved ones and health care professionals.
- Value your hearing as an important part of your overall health.
How can I get my Hearing Number?
Here are a few ways to get your Hearing Number.

See a hearing care professional.
Your hearing care professional, such as an audiologist, will test your hearing. Ask your hearing care professional to tell you your PTA4, which is your Hearing Number.

Get your Hearing Number using a smartphone.
At this time, only iOS devices can provide your Hearing Number. Go to the Apple Store and download the Mimi, Sonic Cloud, or Jacoti app. After testing your hearing in any of these apps, look for your displayed Hearing Number. Coming in fall 2024, the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health will be releasing a free Hearing Number app available for iOS and Android.

Calculate your Hearing Number from your audiogram.
If you have a copy of your hearing test, also known as an audiogram, follow the directions below to calculate your Hearing Number.
Calculate your Hearing Number from your audiogram
If you have a copy of your hearing test, also known as an audiogram, follow the directions below to calculate your Hearing Number.
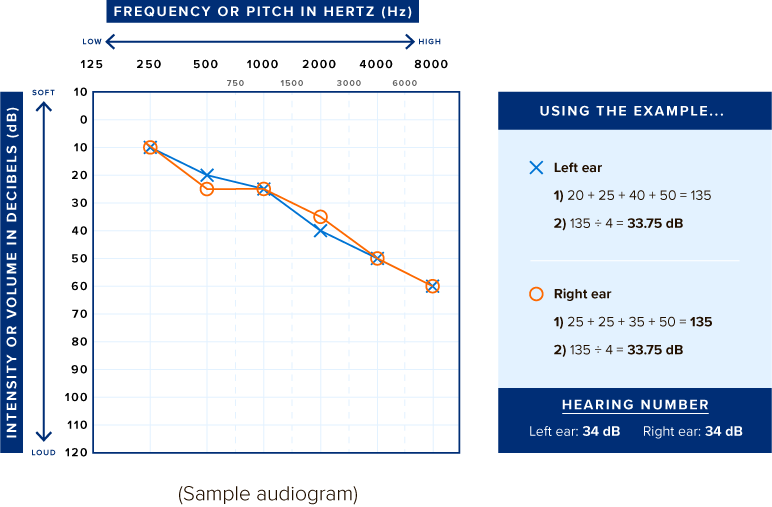
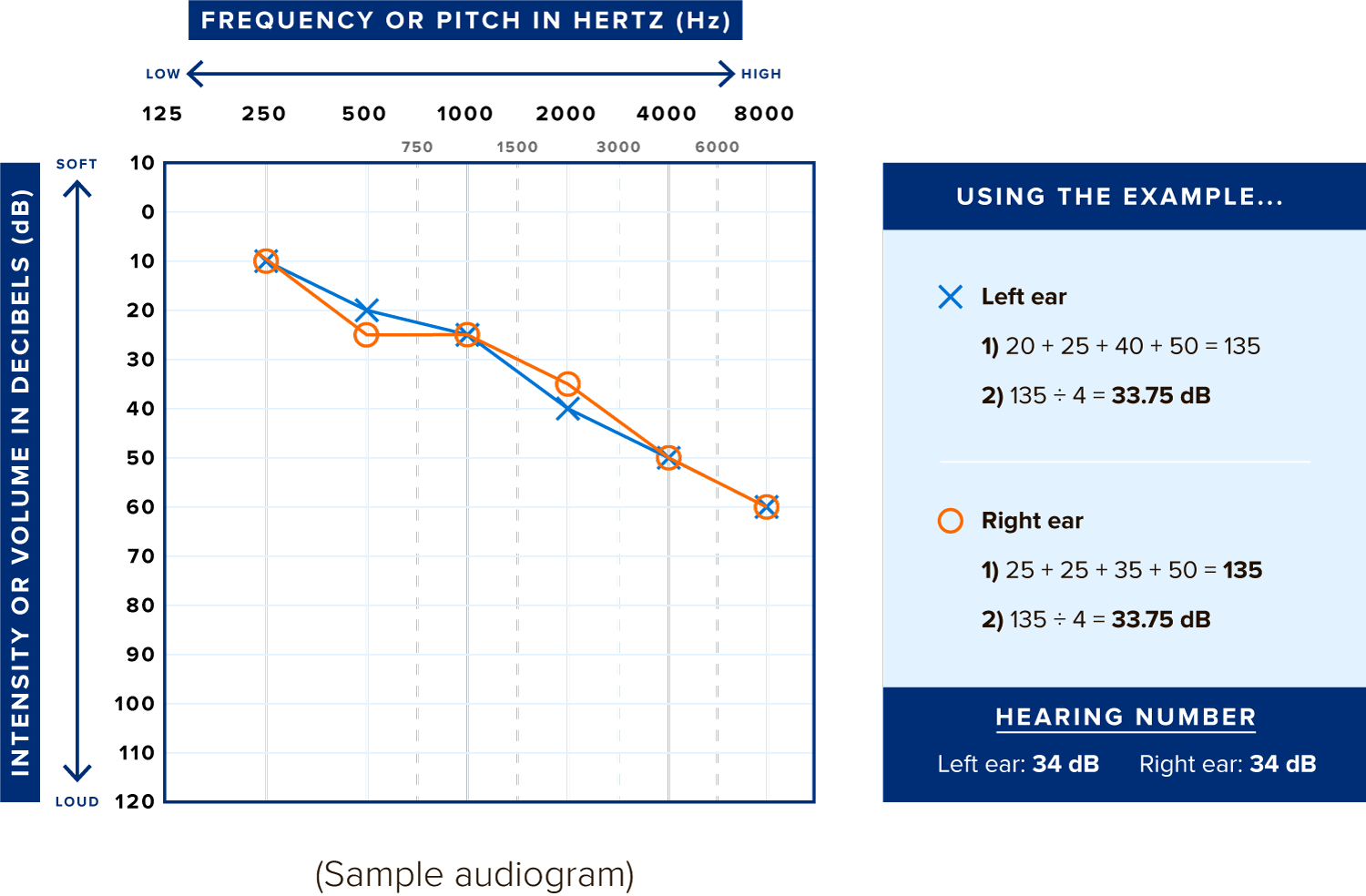
Your audiogram is a graph. Across the top is frequency (Hz). Down the side is decibels (dB). Your audiogram may have many symbols on it. To calculate your Hearing Number, look for the line with the X’s and the line with the O’s.
Start with your left ear, which is the line with the X’s.
- Find 500 Hz on the top of the graph, and then find the X below it. Write down the dB it relates to from the side of the graph. This number will range from 0–120 dB.
- Do the same for the X’s below 1000 Hz, 2000 Hz, and 4000 Hz.
- Add the 4 numbers together and divide the total by 4.
- Round to the nearest whole number. That is your Hearing Number for your left ear!
- Now repeat for your right ear, which is the line with the O’s.